Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
The Constitution of India is considered one of the lengthiest and most detailed documents compared to other countries. The law students will know how difficult the task of remembering 448 articles, 25 parts, and 12 schedules is.
Every law student wants to know “What are the easy ways to remember all the Fundamental Rights? What are the tips to remember Parts of the Constitution? so in this article/blog, we are providing a few practical tips and tricks through which you can remember the Indian Constitution.
Constitution
When the Constitution came into force there were just 22 Parts and now currently we have 25 Parts.
Uski Chupi Fir Dekhnge
Fir Uska Samnder
Us Paar Mje
Chup Sa Rakhna
Fir Talash Sapno Tak Esi
Shayad Ons Ek Ase
Mile Tahare Samunder
| TRICK | PARTS | PROVISIONS |
| Uski | Part-I | THE UNION AND ITS TERRITORY |
| Chupi | Part-II | CITIZENSHIP |
| Fir | Part-III | FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS |
| Dekhnge | Part-IV | DIRECTIVE PRINCIPLES OF STATE POLICY |
| Fir | PART IVA | FUNDAMENTAL DUTIES |
| Uska | PART V | THE UNION |
| Samunder | PART VI | THE STATES |
| Us | PART VIII | UNION TERRITORIES |
| Paar | PART IX | PANCHAYATS |
| Mje | PART IX A | MUNICIPALITIES |
| Chup | PART IXB | CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETIES |
| Sa | PART X | SCHEDULED AND TRIBAL AREAS |
| Rakhna | PART XI | RELATIONS BETWEEN THE UNION AND THE STATES |
| Fir | PART XII | FINANCE, PROPERTY, CONTRACTS, AND SUITS |
| Talash | PART XIII | TRADE, COMMERCE, AND INTERCOURSE WITHIN THE TERRITORY OF INDIA |
| Sapno | PART XIV | SERVICES UNDER THE UNION AND THE STATES |
| Tak | PART XIVA | TRIBUNALS |
| Esi | PART XV | ELECTIONS |
| Shayad | PART XVI | SPECIAL PROVISIONS RELATING TO CERTAIN CLASSES |
| Ons | PART XVII | OFFICIAL LANGUAGE |
| Ek | PART XVIII | EMERGENCY PROVISIONS |
| Mile | PART XIX | MISCELLANEOUS |
| Ase | PART XX | AMENDMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION |
| Tahare | PART XXI | TEMPORARY, TRANSITIONAL, AND SPECIAL PROVISIONS |
| Samunder | PART XXII | SHORT TITLE, COMMENCEMENT, AUTHORITATIVE TEXT IN HINDI AND REPEAL |
Schedule of the Constitution
The Government of India Act in 1935 included 10 Schedules in the Constitution and currently, there are 12 Schedules in the Constitution
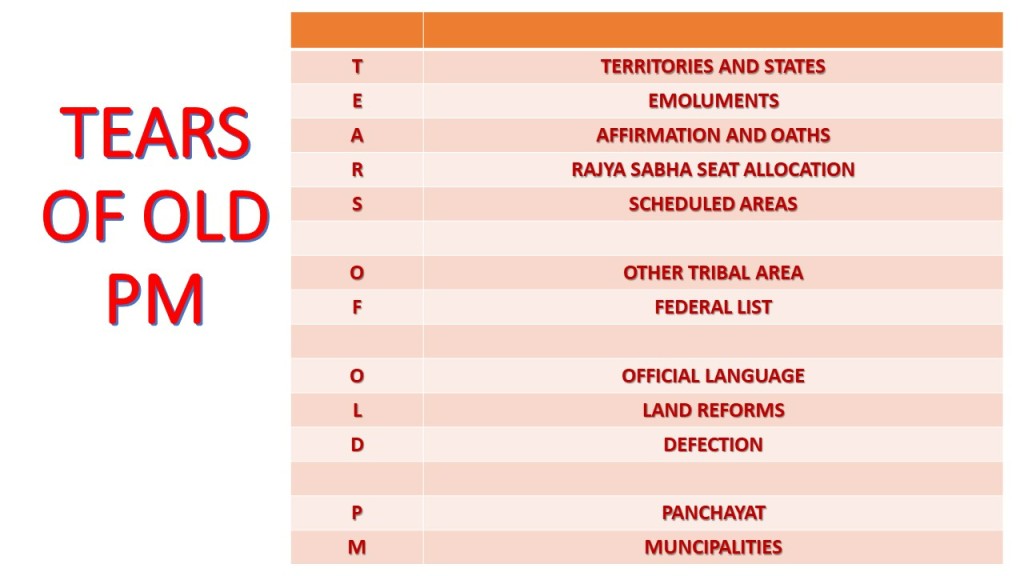
List of Schedules of the Indian Constitution
| Schedules | Features of Schedules |
| First Schedule of Indian Constitution | It contains the name of States and Union Territories Territorial Jurisdiction of states is also included |
| Second Schedule of Indian Constitution | The provisions in relation with allowances, privileges, emoluments of: President of India Governors of Indian States Speaker of Lok Sabha & Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha Chairman of Rajya Sabha & Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha Speaker and Deputy Speaker of Legislative Assemblies of Indian States Chairman and Deputy Chairman of Legislative Councils of the Indian States Supreme Court Judges High Court Judges Comptroller & Auditor General of India (CAG) |
| Third Schedule | It contains the forms of oath and affirmation for: Union Ministers of India Parliament Election Candidates Members of Parliament (MPs) Supreme Court Judges Comptroller and Auditor General State Ministers State Legislature Elections’ Candidates State Legislature Members High Court Judges |
| Fourth Schedule | It contains the provisions in relation to the allocation of seats for States and Union Territories in the Rajya Sabha |
| Fifth Schedule | It contains provisions in relation to the administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes |
| Sixth Schedule | It contains provisions in relation to the administration of tribal areas in the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram |
| Seventh Schedule | This schedule deals with the three legislative lists: Union State Concurrent |
| Eighth Schedule | It deals with the 22 official languages recognized by the Indian Constitution:Assamese Bengali Bodo Dogri (Dongri) Gujarati Hindi Kannada Kashmiri Konkani Mathili (Maithili) Malayalam Manipuri Marathi Nepali Oriya Punjabi Sanskrit Santhali Sindhi Tamil Telugu Urdu |
| Ninth Schedule | It deals with the state acts and regulations of that deal with land reforms andabolition of the zamindari system. It also deals with the acts and regulations of the Parliament dealing with other matters. Note: 1st Amendment Act 1951 added the Ninth Schedule to protect the laws included in it from judicial scrutiny on the ground of violation of fundamental rights. However, in 2007, the Supreme Court ruled that the laws included in this schedule after April 24, 1973, are now open to judicial review |
| Tenth Schedule | It contains provisions relating to disqualification of the members of Parliament and State Legislatures on the ground of defection.Note: This schedule was added by the 52nd Amendment Act of 1985, also known as Anti-defection Law |
| Eleventh Schedule | It contains the provisions that specify the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats. It has 29 matters.Note: This schedule was added by the 73rd Amendment Act of 1992 |
| Twelfth Schedule | It deals with the provisions that specify the powers, authority and responsibilities of Municipalities. It has 18 matters.Note: This schedule was added by the 74th Amendment Act of 1992 |
MUST READ
THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA – PART 1
CITIZENSHIP-PART 2 THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA
FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS-ARTICLE 14 TO 18 (PART 3)
