Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
What is the National language of India? Hindi or English. The big question for all of us
Twitter banter between Ajay Devgn and Kannada actor Kiccha Sudeep has grabbed people’s attention and pushed them to really question whether Hindi is in fact India’s national language.
The debate started when Sudeep reportedly reacted to a comment that used the term “pan-India” to describe the reach of Kannada movies. He said, “Everyone says that a Kannada film was made on a pan-India level but a small correction is that Hindi is not a national language anymore.”
in reply actor Ajay Devgn’s tweet-
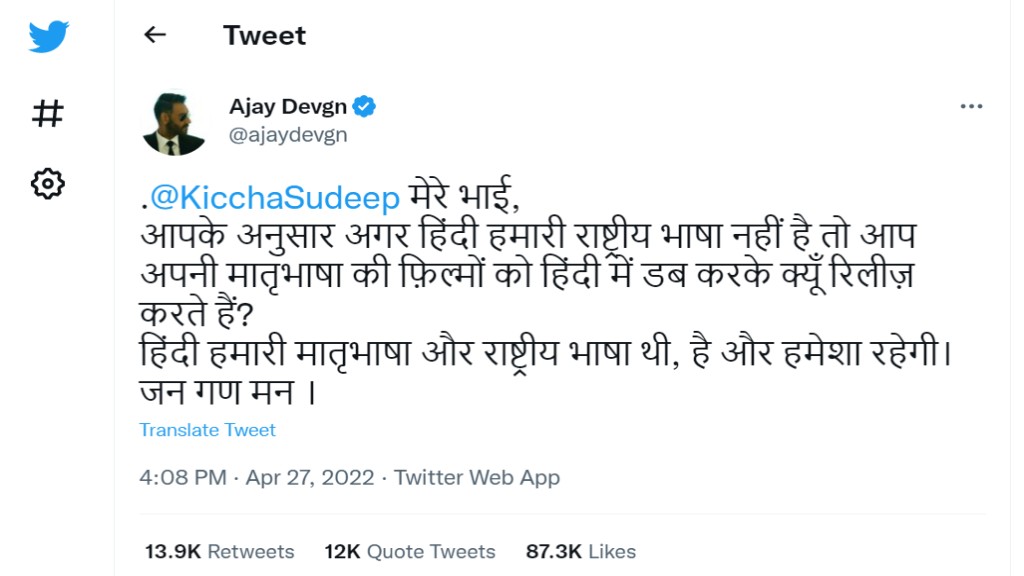
So is Hindi our national language?
India has no national language. Although the majority of northern and western states speak Hindi, it is not the national language of the country.
There is no national language of India as per the constitution, Hindi and English both are considered the official language of India. As per Article 343 of the Indian constitution the official language of the country shall be Hindi in Devanagari script. Initially, after the independence of India, 14 languages were included in the constitution of India.
History of languages of India
There are several official languages in India at the state/territory level. In the present scenario, there are 22 languages spoken in India which are officially registered, these languages are Assamese, Gujarati, Bengali, Hindi, Kashmiri, Kannada, Konkani, Manipuri, Marathi, Malayalam, Odia, Nepali, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu, Bodo, Urdu, Sindhi, Santali, Marathi, and Dogri. State the power to adopt any language as its official language.
At present, there are more than 30 languages that are demanded to be included in the eighth schedule of the constitution
The official languages of British India are English, Urdu, and later Hindi;
English was used for central-level purposes.
The origin of Hindi as official usage was started back in 1900 India’s constitution, adopted in 1950, provided that English would be phased out in favor of Hindi over 15 years, but gave Parliament the right which stipulates the continued use of Hindi, English even after that.
The official languages of colonial India were English Urdu and Hindi. In 1950, when the constitution of India came into effect, it allowed the Indian parliament to continue the use of English. After a few years, in 1964, the government faced resistance from the non-Hindi-speaking people of the country, due to the decision of making Hindi the official language. This was the reason, that both Hindi and English were made the official language of the country.
The National language of India
As we mentioned above, there is no national language in India as per our Constitution. Hindi has certainly been declared a national language. But Hindi is a language spoken by only 45% of India’s population. So that will be a problem for the rest of the population because everyone will be forced to learn Hindi, which is completely impossible.
The official language of India
The Indian Constitution stipulates the use of Hindi and English as the two official languages of government communication. These languages have the right to be represented on the Official Languages Committee and candidates for the exam organized for national civil servants can choose to take the exam in one of these languages.
Difference between national and official language
The primary difference between national and official languages is that while the former is associated with the country’s socio-political and cultural functions, the latter has more to do with the government and its affairs.
That said, an official language does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government, whereas a national language is spoken by a large part of the population of a country, which may or may not is designated an official language.
Schedules Languages of India
| SR. NO | LANGUAGE | AREA |
| 1 | Assamese | Assam |
| 2 | Bengali | West Bengal |
| 3 | Gujarati | Gujarat |
| 4 | Hindi | North India |
| 5 | Kashmiri | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 6 | Kannada | Karnataka |
| 7 | Konkani | Goa |
| 8 | Malayalam | Kerala |
| 9 | Manipuri | Manipur |
| 10 | Marathi | Maharashtra |
| 11 | Nepali | Sikkim, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh |
| 12 | Odia | Odisha |
| 13 | Punjabi | Punjab |
| 14 | Sanskrit | Karnataka (Shivamogga District) |
| 15 | Sindhi | Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh |
| 16 | Tamil | Tamil Nadu |
| 17 | Telugu | Andhra Pradesh, Telangana |
| 18 | Urdu | Jammu & Kashmir, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh |
| 19 | Bodo | Assam and Meghalaya |
| 20 | Santhali | West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha |
| 21 | Maithili | Bihar and Jharkhand |
| 22 | Dogri | Jammu and Himachal Pradesh |
FAQs
Does India have a national language?
India has no official language, but the constitution of India has adopted English and Hindi as the official language.
What is the national language of India as per the constitution of India?
As per the constitution of India, English and Hindi are the official languages, they are not recognized as the national language.
What is the difference between national and official language?
While national language is associated with the country’s socio-political and cultural functions, the official language serves as a language of administration i.e. it has to do with the government and its affairs.
MUST READ
1947 TO 2022 PRIME MINISTERS OF INDIA
A LAWYER WINS 22-YEAR LEGAL BATTLE AGAINST INDIAN RAILWAY
